A triglyceride molecule a breaks down into a monoglyceride. Do saturated fats have double covalent bonds between carbon.
Fats are an oily substance found in the body under the skin or around the organs.

. Listed below are some important characteristics of Lipids. The term lipid is often used to refer to fat but not all lipids are fats. Lipid metabolism entails the oxidation of fatty acids to either generate energy or synthesize new lipids from smaller constituent molecules.
Structurally they are esters of glycerol with three fatty acids called either triacylglycerols or triglycerides. These are of three different types phospholipids triglycerides and steroids. These are also known as natural fats.
Lipid metabolism is associated with carbohydrate metabolism as products of glucose such as acetyl CoA can be converted into lipids. Fats are just one type of lipid a category of molecules united by their inability to mix well with water. The exceptions include the fat-soluble vitamins A D E and K and fatty acids possessing double bonds 6 carbons or less from the ω end the ω end is opposite to the carboxyl end.
Thus there are several types of lipids and these are classified according to their physical properties and functions. A lipid is a fat-soluble molecule. In turn all fats are lipids.
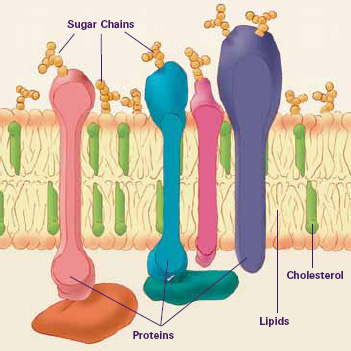
1 Triglycerides make up more than 95 percent of lipids in the diet and are commonly found in fried foods butter milk cheese and some meats. Three basic types of cholesterol are high-density lipoprotein HDL low-density lipoprotein LDL and very-low-density liproprotein VLDL. Lipids are then needed to transport the fat-soluble vitamins A D E and K from your intestines to your blood.
Lipids are an important part of a healthy diet. Lipids also encompass molecules such as fatty acids and their derivatives including tri- di- monoglycerides and phospholipids as well as other sterol -containing metabolites such as cholesterol. Lipids are a class of organic molecules that are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents.
Lipids are a diverse group of biomolecules found in the animal body. B cholesterol andor fat in the blood causes plaque formation in the arteries and consequently heart disease. Oftentimes before the feeling of fullness arrives people overindulge in fat-rich foods.
When fatty foods are swallowed the body responds by enabling the processes controlling digestion to retard the movement of food along the digestive tract thus promoting an overall sense of fullness. Although the term lipid is sometimes used as a synonym for fats fats are a subgroup of lipids called triglycerides. Lipids that are important to our discussion include fats and oils triglycerides or triacyglycerols fatty acids phospholipids and cholesterol.
What are fat and oil molecules sometimes called. Therefore they are often used to describe each other. Therefore the 12 grams of fat in a regular-sized Snickers bar provides 108 fat calories.
When you eat more glucose or carbohydrates than your body needs your system uses acetyl CoA to turn the excess into fat. The three main types of lipids are triacylglycerols also known as triglycerides phospholipids and sterols. This process called lipogenesis creates lipids fat from the acetyl CoA and takes place in the cytoplasm of adipocytes fat cells and hepatocytes liver cells.
These molecules yield high energy and are responsible for different functions within the human body. A cholesterol andor fat in the diet leads to cholesterol andor fat in the blood. Bile acids produced from lipids in your liver allow fat and water to mix in your intestines and aid in the breakdown and absorption of food.
And therefore c cholesterol andor fat in the diet causes heart disease. In fact most lipids used in vivo are synthesized from nonlipid sources. The other major classes of organic compounds nucleic acids proteins and carbohydrates are much more soluble in water than in an organic solvent.
Fat contributes to satiety or the sensation of fullness. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Lipids include fats solid at room temperature and oils liquid at room temperature.
Oils and fats form an important part of a healthy diet. Lipids are oily or greasy nonpolar molecules stored in the adipose tissue of the body. Chemically they can be divided into four main types saturated cis-monounsaturated cis-polyunsaturated and trans fatty acids.
Why is the term lipid used to describe fats. To put it another way lipids are insoluble in water but soluble in at least one organic solvent. Why is the term neutral fat used to describe triglycerides.
Lipids in your body are essential for proper digestion and absorption of food and nutrients. The body uses lipids as an energy store as insulation and to. In simplistic terms the lipid hypothesis is as follows.
Fats are a type of lipids. Lipids are organic biomolecules insoluble in water but in organic solvents these are soluble. Lipids are compounds that are insoluble in water but are soluble in organic solvents such as ether and chloroform.
Lipids tend to be hydrophobic nonpolar and made up mostly of hydrocarbon chains though there are some variations on this which well explore below. Because lipids is the umbrella term for fats oils lecithin and cholesterol. It is these fatty acids that give the functionality to fats.
In very broad terms saturated. Cholesterols impact on health will be discussed later. Lipids are important fats that serve different roles in the human body.
You need fats technically called lipids to survive in addition to other large molecules including carbohydrates proteins and nucleic acids. Lipids are nonpolar molecules which. Yet many people avoid fats in their diet.
Because they are nonpolar. Fats provide 9 calories per gram. Lipids are hydrocarbons molecules consisting of hydrogen and oxygen but they do.
Triglycerides are the largest class of lipids. Lipids are a family of organic compounds composed of fats and oils.

Fatty Acid Definition Structure Functions Properties Examples Britannica


0 Comments